Vitamin Deficiency Symptoms: Nowadays, lifestyle and the struggle to achieve it have become so prominent that people have forgotten to take care of their diet. This ignorance has become one of the causes of the high rate of vitamin deficiency cases. Well, you can find a lot of data on this, but right now our aim is to teach you about types of vitamins, vitamin deficiency, vitamin deficiency diseases, and vitamin deficiency symptoms. Vitamins are part of the school curriculum for chemistry and biology students. Here, students and learners can find data about vitamins that will help them as per their interests.
Read:
What are Vitamins?
Vitamins are essential organic compounds that play a vital role in various biological processes. They play an important role as cofactors and coenzymes, improve immune function, and maintain healthy vision, bones, and skin. Apart from that, there are various other roles for which vitamins are required.
Types of Vitamins
On the basis of their solubility in water and fat, vitamins are classified into water- and fat-soluble vitamins.
|
Water Soluble Vitamins |
Fat Soluble Vitamins |
|
Vitamin C and Vitamin B |
Vitamin A, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, and Vitamin K |
|
Fat-soluble vitamins do not need to be consumed regularly as they can be stored by the body. |
On the other hand, water-soluble vitamins tend to dissolve in water and be excreted from the body. Thus, these need to be consumed regularly through diet. |
What is Vitamin Deficiency?
When a container is not filled with the required amount of water, you call it water deficient, right? Similarly, when a body is deficient in vitamins, it is called vitamin deficiency. There is a minimum amount of each type of vitamin that needs to be consumed. If it is not at the optimal level, then the body struggles to maintain normal physiological functions. Vitamin deficiency and vitamin deficiency diseases can be lethal if not treated on time.
Vitamin Deficiency Diseases
Below is a table that describes all the major vitamins and their vitamin deficiency diseases.
|
Name of Vitamins |
Deficiency diseases |
Recommended daily intake |
|
Vitamin A |
Xerophthalmia (hardening of cornea of eye) Night blindness |
600 µg |
|
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) |
Beri beri (loss of appetite. retarded growth) |
1.4 mg |
|
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) |
Cheilosis (fissuring at corners of mouth and lips). Digestive disorders and burning sensation of the skin. |
1.6 mg |
|
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) |
Convulsions |
2 mg |
|
Vitamin B12 |
Pernicious anaemia (RBC deficient in haemoglobin) |
6 µg |
|
Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) |
Scurvy (bleeding gums) |
75 mg |
|
Vitamin D |
Rickets (bone deformities in children) and osteomalacia (soft bones and joint pain in adults) |
5 µg |
|
Vitamin E |
Increased fragility of RBCs and muscular weakness |
10 mg |
|
Vitamin K |
Increased blood clotting time |
80 µg |
Source: NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Textbook
The given quantities of daily intake may vary depending on the person’s gender and age. Prefer to check their individual recommended daily doses for better clarification.
Read: Know How Students Can Improve Their Concentration
Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin Deficiency
The signs and symptoms of vitamin deficiency can vary depending on the specific vitamin lacking in your diet. However, some common signs include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Brittle nails and hair
- Skin issues, such as dryness or rashes
- Muscle cramps or spasms
- Vision problems
- Cognitive issues, such as brain fog or memory problems
- Digestive problems
- Susceptibility to infections
- Bone and joint pain
Vitamins and Their Sources
We can get vitamins from various food sources which are easily available. Check the table to know vitamin sources.
|
Name of Vitamins |
Dietary Vitamin Sources |
|
|
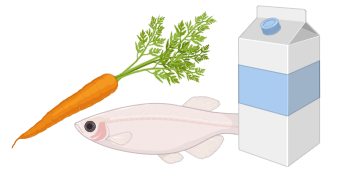
Vitamin A |
Fish liver oil, carrots, butter and milk |
 |
|
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) |
Yeast, milk, green vegetables and cereals |
 |
|
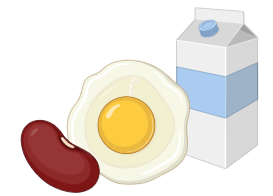
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) |
Milk, egg white, liver, kidney |
 |
|
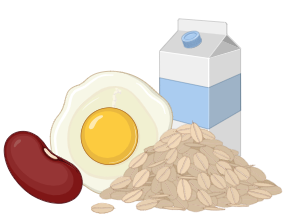
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) |
Yeast. milk. egg yolk, cereals and grams |
 |
|
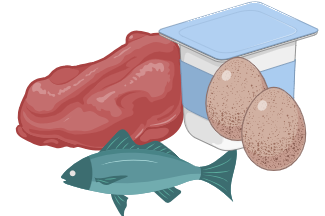
Vitamin B12 |
Meat, fish, egg and curd |
 |
|
Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) |
Citrus fruits, Amla and green leafy vegetables |
 |
|
Vitamin D |
Exposure to sunlight, fish and egg yolk |
 |
|
Vitamin E |
Vegetable oils like wheat germ oil, and sunflower oil. etc. |
 |
|
Vitamin K |
Green leafy vegetables |
 |
Source: NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Textbook
Read: 7 Best Asanas to Boost Memory and Concentration
Prevention of Vitamin Deficiency
- Consume a variety of fruits and vegetables of different colours.
- If you have specific dietary restrictions or medical conditions that limit your vitamin intake, consider taking supplements.
- For vitamin D, spend some time outdoors in the sun.
- If you suspect a deficiency or have symptoms, seek advice from a healthcare provider.
- Include fortified foods.
After reading this post, you might have an idea about how important the consumption of vitamins is and how it may lead to vitamin deficiency. Vitamin deficiencies create vitamin deficiency diseases that have specific vitamin deficiency symptoms. If these vitamin deficiency symptoms are not treated well, they may have serious consequences.
Also Read:
