Maths 12th Application of Derivatives MCQs: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) conducts the annual final board exam for class 12, which is considered among the hardest and most important exams in the country for students.
The board exam consists of a vast syllabus, and the question paper comprises various types of questions like short answer, long-answer and MCQs. The objective multiple choice questions are often confusing and time-taking so every student should practice them thoroughly before exams.
Maths is a popular subject choice for students, but it’s no easy task to ace CBSE Class 12 mathematics. MCQs for Application of Derivatives and other calculus chapters trouble students quite a lot. To counter that, we bring you the following questions for practice. From easy to difficult, all levels of questions are covered.
You can check out the MCQs for CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives below.
Related:
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability MCQs
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 2 Inverse Trigonometric Functions MCQs
MCQs for CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives
Question 1: The function f(x) = x + cos x is
(a) Always increasing
(b) Always decreasing
(c) Increasing for a certain range of x
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) Always increasing
Question 2: The tangent to the curve y = e2x at the point (0, 1) meets the x-axis at
(a) (0, 1)
(b) (2, 0)
(c) (-1/2, 0)
(d) (-2, 0)
Answer: (-1/2,0)
Related: CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus 2024-24: 12th Maths Syllabus Download PDF
Question 3: The side of an equilateral triangle is increasing at the rate of 2 cm/s. The rate at which area increases when the side is 10 is
(a) 10 cm2/s
(b) 10/3 cm2/s
(c) √3 cm2/s
(d) 10√3 cm2/s
Answer: (d) 10√3 cm2/s
Question 4: If f(x) = 3x4 – 4x2 + 5, then the interval for which f(x) satisfy all the conditions of Rolle’s theorem, is
(a) (0, 2)
(b) (-1, 1)
(c) (-1, 0)
(d) (-1, 2)
Answer: (b) (-1, 1)
Also Check: NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths PDF: Updated for 2024-24
Question 5: A ladder, 5 meter long, standing on a horizontal floor leans against a vertical wall. If the top of the ladder slides downwards at the rate of 10cm/sec, then the rate at which the angle between the floor and the ladder is decreasing when lower end of ladder is 2 metres from the wall is
(a) 1/10 rad/sec
(b) 1/20 rad/sec
(c) 20 rad/sec
(d) 10 rad/sec
Answer: (b) 1/20 rad/sec
Question 6: The point(s) on the curve y = x², at which y-coordinate is changing six times as fast as x-coordinate is/are
(a) (6, 2)
(b) (2, 4)
(c) (3, 9)
(d) (3, 9), (9, 3)
Answer: (c) (3, 9)
Question 7: The function f(x) = x5 – 5x4 + 5x3 – 1 has
(a) one minima and two maxima
(b) two minima and one maxima
(c) two minima and two maxima
(d) one minima and one maxima
Answer: (d) one minima and one maxima
Related: CBSE Class 12 Maths Sample Paper 2024-24 with Solutions PDF – Download Model Paper
Question 8: The line y = x + 1 is a tangent to the curve y² = 4x at the point
(a) (1, 2)
(b) (2, 1)
(c) (-1, 2)
(d) (1, -2)
Answer: (a) (1, 2)
Question 9: 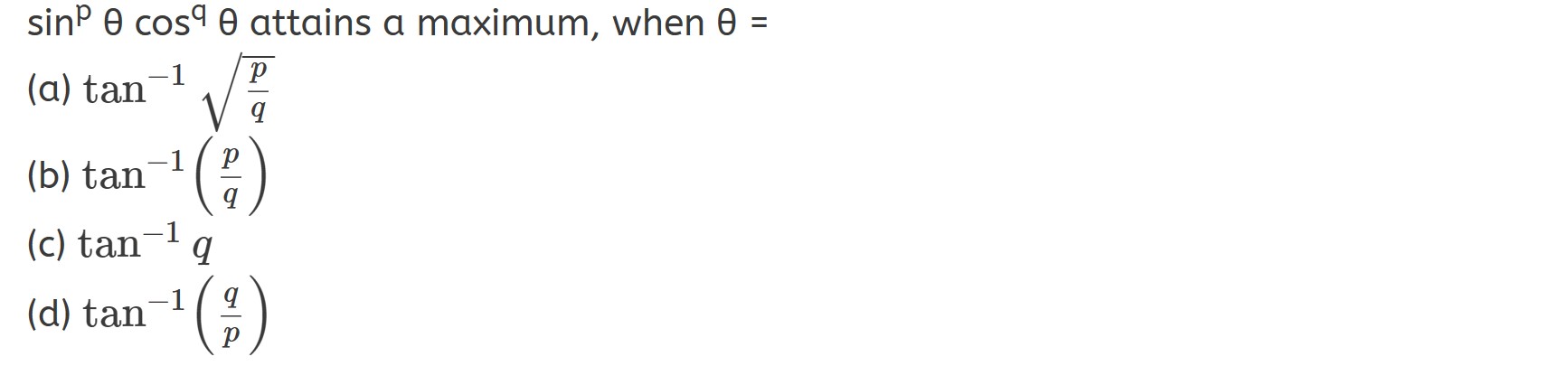
Answer: 
Question 10: If x increases at the rate of 2 m/sec at the instant when x = 3 m, y = 1 m, at what rate must y be changing in order that the function 2xy – 3x2y shall be neither increasing nor decreasing?
(a) 32/21 m/sec; increasing
(b) 32/21 m/sec; decreasing
(c) 8/21 m/sec; increasing
(d) 8/21 m/sec; decreasing
Answer: (b) 32/21 m/sec; decreasing
Recommended:
