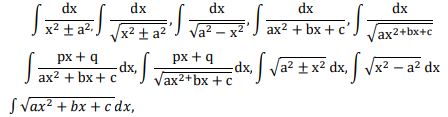Maths Syllabus Class 12 2022 – 2023: CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Revised Syllabus for the academic session 2022-2023 is provided here for students to download in PDF. Students must go through this rationalised syllabus to know the course content based on which the CBSE Class 12 Maths Board Examination 2023 will be conducted. Students must check this reduced syllabus to ensure that nothing is left to revise for the CBSE Class 12 Maths exam to be held on March 11, 2023.
Must Read:
CBSE Class 12 Maths DELETED Syllabus 2022-23
CBSE Class 12 Maths Sample Paper 2022-23
Maths Syllabus Class 12th 2022 – 23:
CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus 2022-23 :Course Structure
One Paper
Max Marks: 80
|
No. |
Units |
Marks |
|
I |
Relations and Functions |
08 |
|
II |
Algebra |
10 |
|
III |
Calculus |
35 |
|
IV |
Vectors and Three – Dimensional Geometry |
14 |
|
V |
Linear Programming |
05 |
|
VI |
Probability |
08 |
|
|
Total |
80 |
|
|
Internal Assessment |
20 |
Unit-1: Relations and Functions
1. Relations and Functions
Types of relations: reflexive, symmetric, transitive and equivalence relations. One to one and onto functions.
2. Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Definition, range, domain, principal value branch. Graphs of inverse trigonometric functions.
Unit-2: Algebra
1. Matrices
Concept, notation, order, equality, types of matrices, zero and identity matrix, transpose of a matrix, symmetric and skew symmetric matrices. Operation on matrices: Addition and multiplication and multiplication with a scalar. Simple properties of addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication. Oncommutativity of multiplication of matrices and existence of non-zero matrices whose product is the zero matrix (restrict to square matrices of order 2). Invertible matrices and proof of the uniqueness of inverse, if it exists; (Here all matrices will have real entries).
2. Determinants
Determinant of a square matrix (up to 3 x 3 matrices), minors, co-factors and applications of determinants in finding the area of a triangle. Adjoint and inverse of a square matrix. Consistency, inconsistency and number of solutions of system of linear equations by examples, solving system of linear equations in two or three variables (having unique solution) using inverse of a matrix.
Unit-3: Calculus
1. Continuity and Differentiability
Continuity and differentiability, chain rule, derivative of inverse trigonometric functions, 𝑙𝑖𝑘𝑒 sin−1 𝑥 , cos−1 𝑥 and tan−1 𝑥, derivative of implicit functions. Concept of exponential and logarithmic functions. Derivatives of logarithmic and exponential functions. Logarithmic differentiation, derivative of functions expressed in parametric forms. Second order derivatives.
2. Applications of Derivatives
Applications of derivatives: rate of change of bodies, increasing/decreasing functions, maxima and minima (first derivative test motivated geometrically and second derivative test given as a provable tool). Simple problems (that illustrate basic principles and understanding of the subject as well as reallife situations).
3. Integrals
Integration as inverse process of differentiation. Integration of a variety of functions by substitution, by partial fractions and by parts, Evaluation of simple integrals of the following types and problems based on them.
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (without proof). Basic properties of definite integrals and evaluation of definite integrals.
4. Applications of the Integrals
Applications in finding the area under simple curves, especially lines, circles/ parabolas/ellipses (in standard form only)
5. Differential Equations
Definition, order and degree, general and particular solutions of a differential equation. Solution of differential equations by method of separation of variables, solutions of homogeneous differential equations of first order and first degree. Solutions of linear differential equation of the type:
Unit-4: Vectors and Three-Dimensional Geometry
1. Vectors
Vectors and scalars, magnitude and direction of a vector. Direction cosines and direction ratios of a vector. Types of vectors (equal, unit, zero, parallel and collinear vectors), position vector of a point, negative of a vector, components of a vector, addition of vectors, multiplication of a vector by a scalar, position vector of a point dividing a line segment in a given ratio. Definition, Geometrical Interpretation, properties and application of scalar (dot) product of vectors, vector (cross) product of vectors.
2. Three – dimensional Geometry
Direction cosines and direction ratios of a line joining two points. Cartesian equation and vector equation of a line, skew lines, shortest distance between two lines. Angle between two lines.
Unit-5: Linear Programming
1. Linear Programming
Introduction, related terminology such as constraints, objective function, optimization, graphical method of solution for problems in two variables, feasible and infeasible regions (bounded or unbounded), feasible and infeasible solutions, optimal feasible solutions (up to three non-trivial constraints).
Unit-6: Probability
1. Probability
Conditional probability, multiplication theorem on probability, independent events, total probability, Bayes’ theorem, Random variable and its probability distribution, mean of random variable.
CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Question Paper Design 2022-23
(Code No. 041)
|
S. No. |
Typology of Questions |
Total Marks |
% Weightage |
|
1 |
Remembering: Exhibit memory of previously learned material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers. Understanding: Demonstrate understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating main ideas. |
44 |
55 |
|
2 |
Applying: Solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way. |
20 |
25 |
|
3 |
Analysing : Examine and break information into parts by identifying motives or causes. Make inferences and find evidence to support generalizations Evaluating: Present and defend opinions by making judgments about information, validity of ideas, or quality of work based on a set of criteria. Creating: Compile information together in a different way by combining elements in a new pattern or proposing alternative solutions |
16 |
20 |
|
Total |
80 |
100 |
1. No chapter wise weightage. Care to be taken to cover all the chapters
2. Suitable internal variations may be made for generating various templates keeping the overall weightage to different form of questions and typology of questions same.
Choice(s): There will be no overall choice in the question paper. However, 33% internal choices will be given in all the sections.
Note: For activities NCERT Lab Manual may be referred.
CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus 2022-23: Internal Assessment – 20 MARKS
- Periodic Tests ( Best 2 out of 3 tests conducted) 10 Marks
- Mathematics Activities 10 Marks
Conduct of Periodic Tests:
Periodic Test is a Pen and Paper assessment which is to be conducted by the respective subject teacher. The format of periodic test must have questions items with a balance mix, such as, very short answer (VSA), short answer (SA) and long answer (LA) to effectively assess the knowledge, understanding, application, skills, analysis, evaluation and synthesis. Depending on the nature of subject, the subject teacher will have the liberty of incorporating any other types of questions too. The modalities of the PT are as follows:
a) Mode: The periodic test is to be taken in the form of pen-paper test.
b) Schedule: In the entire Academic Year, three Periodic Tests in each subject may be conducted as follows:
This is only a suggestive schedule and schools may conduct periodic tests as per their convenience. The winter bound schools would develop their own schedule with similar time gaps between two consecutive tests.
c) Average of Marks: Once schools complete the conduct of all the three periodic tests, they will convert the weightage of each of the three tests into ten marks each for identifying best two tests. The best two will be taken into consideration and the average of the two shall be taken as the final marks for PT.
d) The school will ensure simple documentation to keep a record of performance as suggested in detail circular no.Acad-05/2017.
e) Sharing of Feedback/Performance: The students’ achievement in each test must be shared with the students and their parents to give them an overview of the level of learning that has taken place during different periods. Feedback will help parents formulate interventions (conducive ambience, support materials, motivation and morale-boosting) to further enhance learning. A teacher, while sharing the feedback with student or parent, should be empathetic, non- judgmental and motivating. It is recommended that the teacher share best examples/performances of IA with the class to motivate all learn.
Assessment of Activity Work:
Throughout the year any 10 activities shall be performed by the student from the activities given in the NCERT Laboratory Manual for the respective class (XI or XII) which is available on the link: http://www.ncert.nic.in/exemplar/labmanuals.htmla record of the same may be kept by the student. An year end test on the activity may be conducted.
The weightage are as under:
- The activities performed by the student throughout the year and record keeping : 5 marks
- Assessment of the activity performed during the year end test: 3 marks
- Viva-voce: 2 marks
CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus 2022-23:Prescribed Books
- Mathematics Part I – Textbook for Class XII, NCERT Publication
- Mathematics Part II – Textbook for Class XII, NCERT Publication
- Mathematics Exemplar Problem for Class XII, Published by NCERT
- Mathematics Lab Manual class XII, published by NCERT
The link to download the syllabus is mentioned below:
Also Read|
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Maths
Related Syllabus: