New School Curriculum, NCF 2023: The new National Curriculum Framework 2023 was released on August 23, 2023. The NCF 2023 follows the guidelines and recommendations of the National Education Policy 2023 (NEP 2020). To finalise the NCF 2023, a mandate document was released on April 29, 2022, by Shri Dharmendra Pradhan, Union Education Minister, at a function held at the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru. He said, “The National Education Policy 2020 is the ‘Philosophy’, the National Curriculum Framework is the ‘Pathway, and the mandate document released today is the ‘Constitution’ to champion the changing demands of the 21st century and positively impact the future. The 1.4 section of the NCF highlights the stage design of the school curriculum, which is expected to be followed from now on. This stage design divides the school curriculum into four stages: foundational, preparatory, middle, and secondary, based on the age of students. Check out the complete stage-wise details here.
Read: All NCFs Published Till Now
Stage Design of NCF 2023
The National Curriculum Framework is based on the National Education Policy 2020 and has divided the school curriculum into four stages as per the NEP 2020 recommendations. The four stages are as follows:
- Foundational Stage
- Preparatory Stage
- Middle Stage
- Secondary Stage
In the content below, we will discuss these stages one by one. These will help you know the recent revisions and suggestions for the school curriculum.
Foundational Stage
|
Age Group |
The base of Learning Standards |
Pedagogy |
Assessment |
Aim |
Tool of this Stage |
|
Between 3 and 8 |
Domains of development (Physical Development, Socio-emotional and Ethical Development, Cognitive Development, Aesthetic and Cultural Development, and Language and Literacy Development + Positive Learning Habits) |
largely play-based and emphasises nurturing, caring relationships between the Teacher and the children. There should be a balance between self-paced individual learning and group activities. Systematic guidance is required for developing Foundational Literacy and Numeracy. |
Assessments are conducted largely in the form of qualitative observations by Teachers. Grades 1 and 2, worksheets can be a source of information on children’s learning for the Teacher. Explicit tests and examinations are deemed to be inappropriate for this Stage. |
Children learn two languages (R1 and R2) and are expected to achieve Foundational Literacy in R1 by the end of this Stage. |
Concrete play materials, such as toys, puzzles, picture books, and manipulatives during the first three years. Textbooks/ playbooks/ workbooks are recommended only from Grade 1. Children’s literature is a particularly important source of content for this Stage. |
Preparatory Stage
|
Age Group |
The base of Learning Standards |
Pedagogy |
Assessment |
Aim |
Tool of this Stage |
|
Between 8 and 11 |
The Learning Standards for this Stage have been set for two languages within Language Education (R1 and R2), Mathematics, Art Education, Physical Education, and The World Around Us (as an interdisciplinary area of study). Work and pre-vocational skills are included as part of The World Around Us curriculum. |
Activity – and discovery-based pedagogy should continue to play a big role in the Preparatory Stage classroom. |
Short formal written assessments are appropriate for this Stage. Teachers’ observation of students’ work continues to form an important assessment mechanism. Periodic summative assessments can be utilised to supplement the more regular formative assessments. Summative assessments at the end of this Stage should be based on the Competencies defined in the Learning Standards. |
Encourage students to be active participants in more formal classroom settings. |
Content can be presented slightly more through textbooks while concrete materials and experiences still form the core of content presentation. The World Around Us (TWAU), in particular, should rely more on activities and experiences, rather than presented as inert facts in textbooks. |
Middle Stage
|
Age Group |
The base of Learning Standards |
Pedagogy |
Assessment |
Aim |
Tool of this Stage |
|
Between 11 and 14 |
Students need to learn three languages (R1, R2, and R3) in this Stage. Learning Standards are set for these languages as well as for Mathematics, Art Education, and Physical Education. Science Education and Social Science Education have separate sets of Learning Standards, and Vocational Education finds its own curricular space and Learning Standards |
The pedagogy adopted in this Stage should be a judicious balance of direct instruction as well as opportunities for exploration and inquiry. Building on prior knowledge and opportunities to learn from errors become important considerations for instructional strategies. There should be a constant focus on the methods of inquiry within each Curricular Area. |
Assessments can be more formal and explicit. Assessment design has a very important role to play in shifting the focus from content retention to conceptual understanding and fluency in the methods of inquiry. Students should be given opportunities to engage with higher-order capacities of analysis and synthesis through meaningful, yet challenging, assessments. Summative assessments at the end of this Stage should again be based on the Competencies defined in the Learning Standards. |
Students are expected to engage with unfamiliar contexts and situations. The language used in the content should assist students in developing academic linguistic proficiency |
Well-designed textbooks that reflect the specific goals of the Learning Standards have a very significant role to play in presenting content in easy and comprehensible formats in this journey from concrete to abstract. |
Secondary Stage
Phase 1-Grades 9 and 10:
All students would continue to engage with all the Curricular Areas as in the Middle Stage.
In addition, students would study Environmental Education as an Interdisciplinary Area of study. They would develop capacities for reasoning and argumentation for issues in the public sphere along with ethical and moral reasoning. They would use these capacities in the context of Environment Education.
Learning Standards have been set for these areas of study
Phase 2 — Grades 11 and 12:
|
Age Group |
The base of Learning Standards |
Pedagogy |
Aim |
Tool of this Stage |
|
Between 14 and 18 |
Choice-based courses are to be offered to enable flexibility and choice for students and to remove hard separations between disciplines and academic areas. |
Pedagogy at this Stage should expect more independent learning from the students. More opportunities for self-study and group work should be encouraged. Classroom interactions should also be diverse — didactic, Socratic, and inquiry-based methods are all appropriate for this Stage. |
This scheme allows for both breadth of study as well as gaining disciplinary depth. To allow for interesting combinations, there should be no further restrictions for students to choose specific streams. |
Textbooks play a significant role in organising content in Grades 9 and 10. In Grades 11 and 12, students should be encouraged to source content from multiple channels. Course compendiums can be utilised in Grades 11 and 12 to make the choice of content more dynamic and flexible. |
|
Assessments and Board Examinations: |
|
i. Students should be given opportunities to engage with higher-order capacities of analysis and synthesis through meaningful yet challenging assessments. ii. Board examinations for Grade 10 should be based on the Competencies set for each of the Curricular Goals in that area. Art Education, Physical Education, and Vocation Education would have local assessments with Board certification. iii. To get a Grade 12 certificate, the students should pass the following Board Examinations: 1) 2 examinations in Languages 2) 4 examinations from at least 2 Groups (with one additional optional exam) 3) Subjects in Group 2 (Art Education, Physical Education, and Vocational Education) would have local assessments with Board certification. |
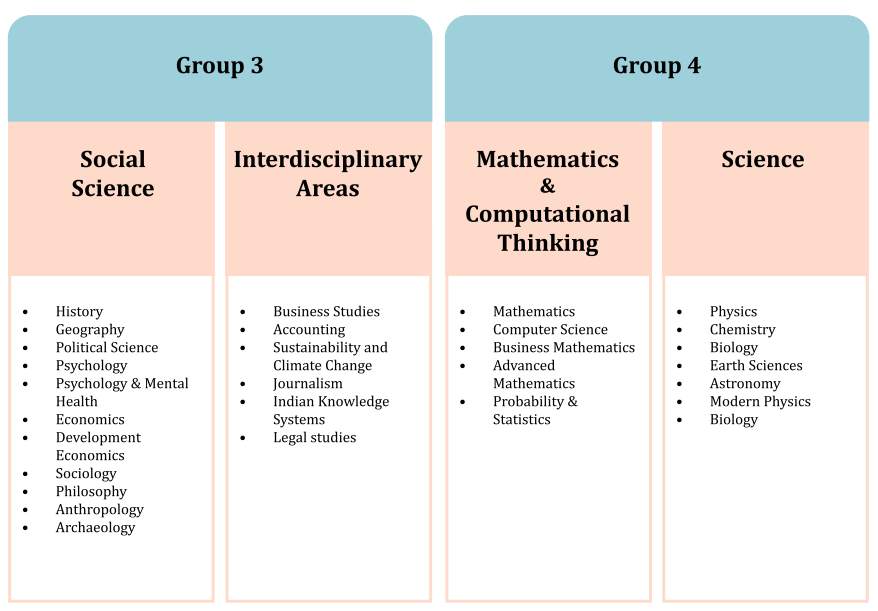
- Students need to choose four subjects (with an optional fifth subject) from at least two of the following three groups (see Figure below):
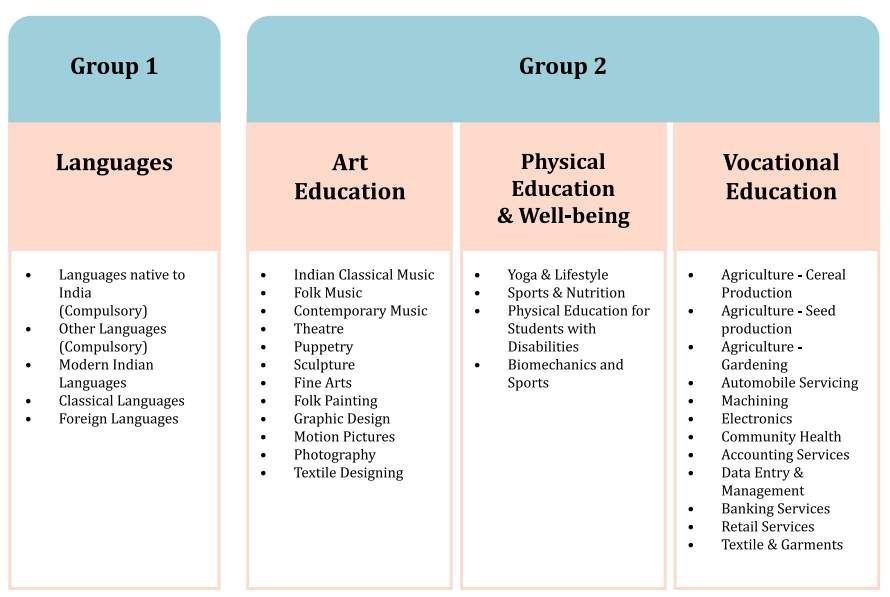
1) Group 2: Art Education, Physical Education, Vocational Education
2) Group 3: Social Science and Humanities, Interdisciplinary Areas
3) Group 4: Science, Mathematics and Computational Thinking
- An illustrative list of subjects that can be made available within each Group is given below.
- Some illustrative combinations possible with this scheme are given in Figure below

The content you read here was directly picked from the National Curriculum Framework 2023 to avoid the transmission of false or misleading information. To have a thorough review of Stage Design 2023 click on the link below and download the PDF.
Also Read:
